Description
This guide is an overview and outline on the redundancy options available with HELIOS. It also discusses the importance of utilizing a Stack for settings to be shared across multiple processors.
What is Redundancy?
System redundancy refers to the practice of including duplicate components or processors within a larger system to ensure reliability and availability. This provides backup in case one component fails, thereby preventing a single point of failure from disrupting the entire system's operation. Redundancy is especially important for events that can't be reproduced, or "failure is not an option", such as concerts, real-time events, or live broadcasts.
Redundancy Modes Offered by HELIOS
HELOS offers different types of redundancy, depending on how resilient the system needs to be vs. how much extra gear can be facilitated.
| Redundancy Mode | HELIOS | Fiber | Switch | Ethernet Cable | Redundancy Level |
None | O | O | O | O | 0 (No redundancy) |
| Single HELIOS Single Switch SeamlessLoop | O | O | O | X | 1 |
| Single HELIOS Dual Switch SeamlessLoop | O | X | X | X | 2 |
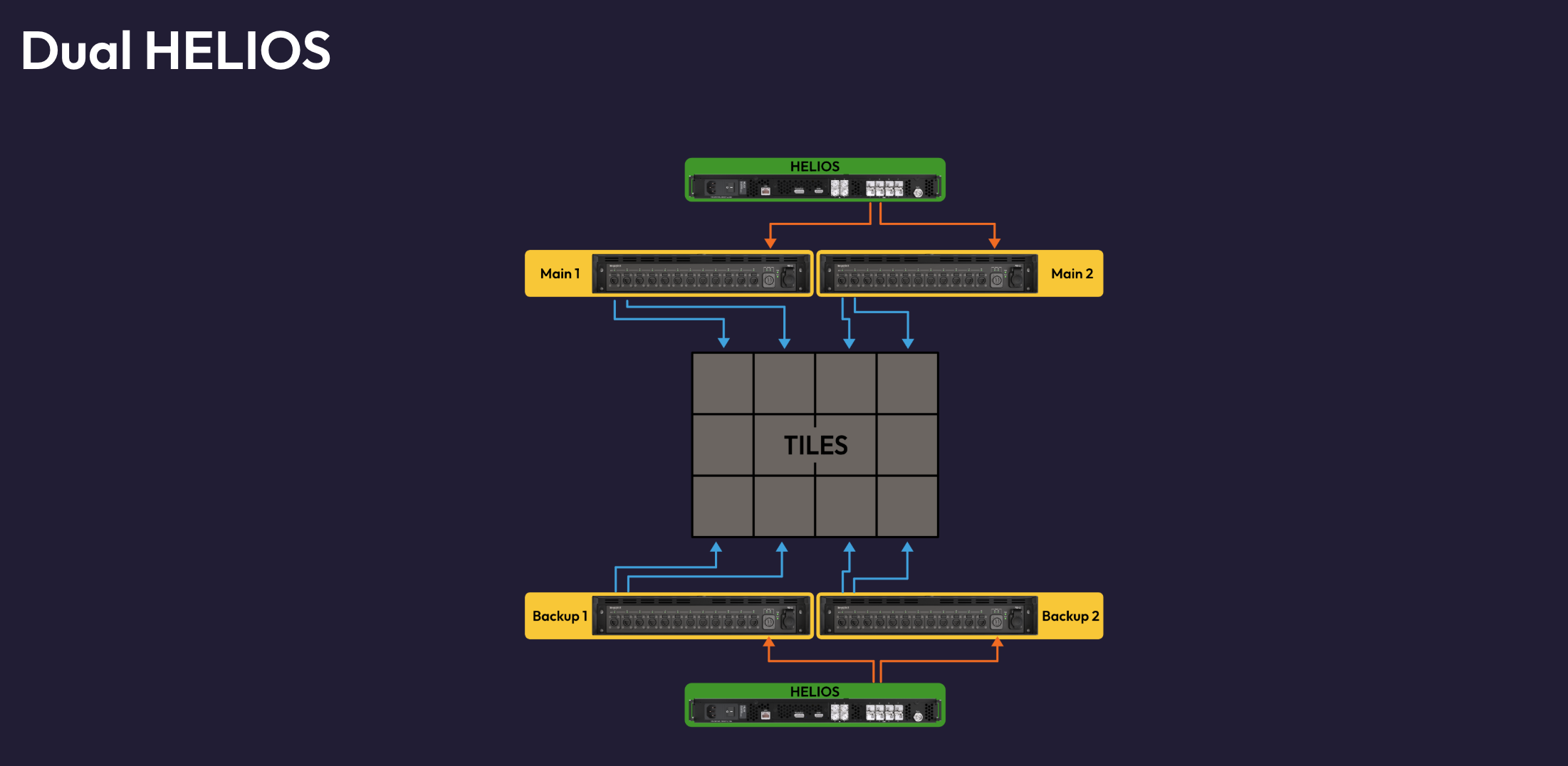
| Dual HELIOS Failover | X | X | X | X | 3 |
| Dual HELIOS Seamless | X | X | X | X | 4 (Most redundancy) |
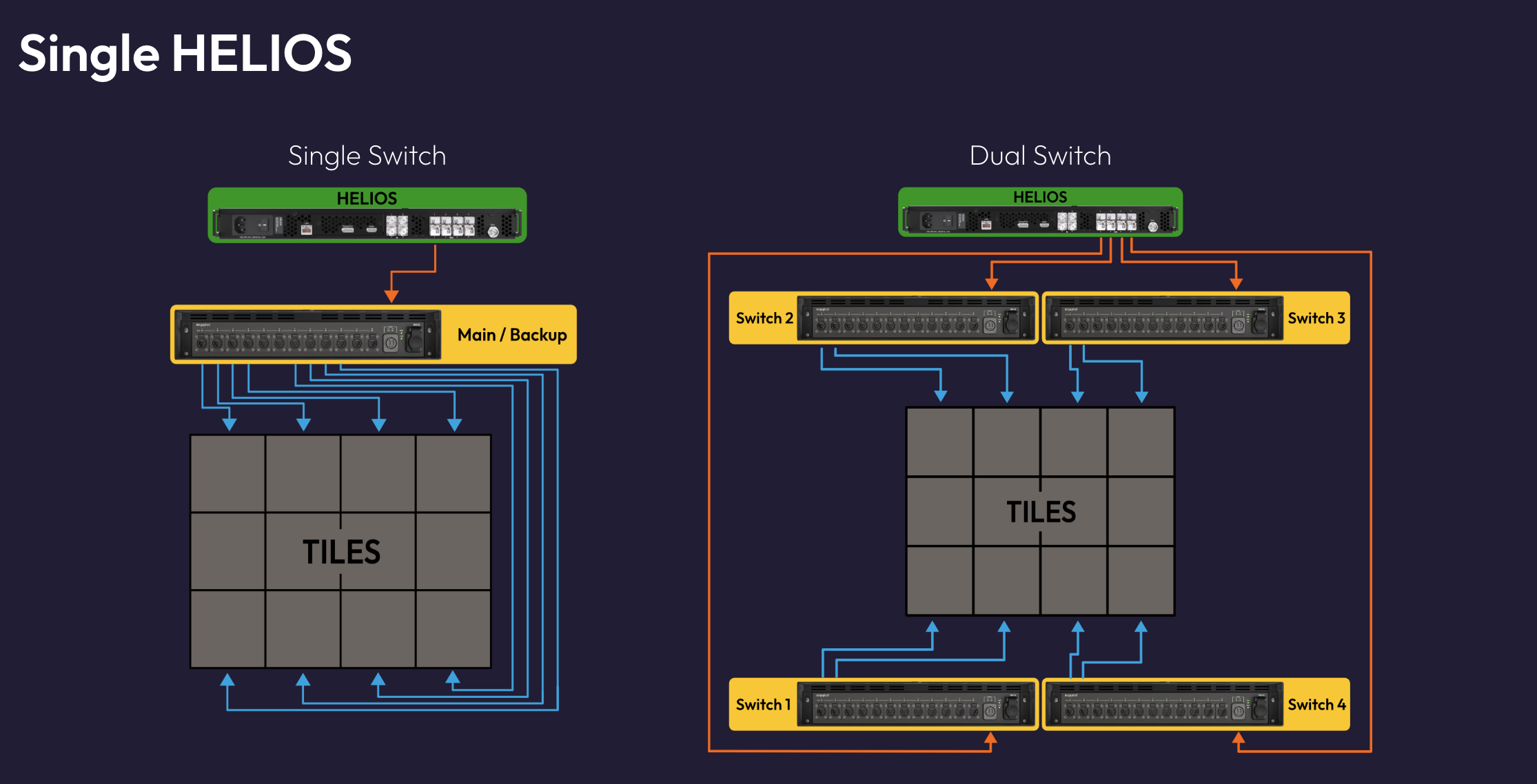
Note - There are no limitations on cabling. You can mix and match cabling as you please and HELIOS will automatically detect the redundant pathway.
Getting Started with Multiple Processors (Stacking)
Before starting to configure a redundant setup with multiple HELIOS units, it's always a good idea to create a stack. A stack is a grouping of HELIOS processors that enables settings to be transferred from one processor to another automatically. This ensures that any changes you make on the Main processor get reflected onto the Backup processor.
Stack Processors before mapping. The order in which processors are stacked matters!
If you have already mapped the tiles on your main processor, it is suggested that you unplug the backup cables, enable Stacking on the main (A) HELIOS first, create the stack, then add the backup HELIOS.
Once the backup is in the Stack, go ahead and plug the backup cables in and the mapping will be correct across both. Note - The cable paths in the Mapping pane will show as opposite between main and backup. This is expected and correct.
Settings are propagated based on how long processors have been part of the stack (newly added processors will copy the settings from the existing).
Dual HELIOS: Failover vs. Seamless Modes
When deciding between Failover and Seamless modes, it's important to understand the key differences in behavior, requirements, and system impact.
In Failover Mode:
In the event of a system failure, there will be a brief 1-2 second interruption (blackout) on the LED display.
Different content sources can be delivered to each HELIOS system.
HELIOS devices do not need to be synchronized.
In Seamless Mode:
System failures result in a seamless transition. Viewing audiences will not notice that an issue has occurred.
The exact same content must be delivered to both HELIOS systems.
All content sources and HELIOS systems need to be synchronized together so that the matching content is delivered at the same time.
Seamless mode essentially sends the same packets to the tiles from both route directions, and the tiles will display whichever packet gets to them first. This allows for a virtually seamless transition in the event of an issue occurring, but requires stricter content source configurations.